Beginner’s Guide to Web3 Security: Guide to Avoiding Fake Wallets and Private Key/Mnemonic Phrase Compromises
Author: SlowMist
Background
Wallets play a crucial role in the Web3 world. They are not only tools for storing digital assets but also essential for users to conduct transactions and access DApps. In the previous edition of our Web3 Security Guide, we introduced the different types of wallets and highlighted common risks, helping readers develop a basic understanding of wallet security. As cryptocurrency and blockchain technology become more widespread, cybercriminals are increasingly targeting Web3 users’ funds. According to reports received by the SlowMist security team, many users have fallen victim to theft by downloading or purchasing fake wallets. Therefore, in this edition, we will explore why users download or purchase fake wallets, the risks of private key/mnemonic phrase leaks, and provide a series of security recommendations to help users protect their funds.
Downloading Fake Wallets
Many users download wallets from alternative sources because their mobile devices do not support Google Play Store or due to network issues.
Third-Party Download Sites
Some users download wallets from third-party sites like apkcombo and apkpure. These sites often claim that their apps are mirrored from Google Play Store, but how reliable are they? The SlowMist security team conducted an investigation into fake Web3 wallets from third-party sources and found that the wallet version provided by apkcombo did not actually exist. Once users create a wallet or import a mnemonic phrase in the fake wallet’s interface, the fake wallet sends the mnemonic phrase and other information to a phishing website’s server.
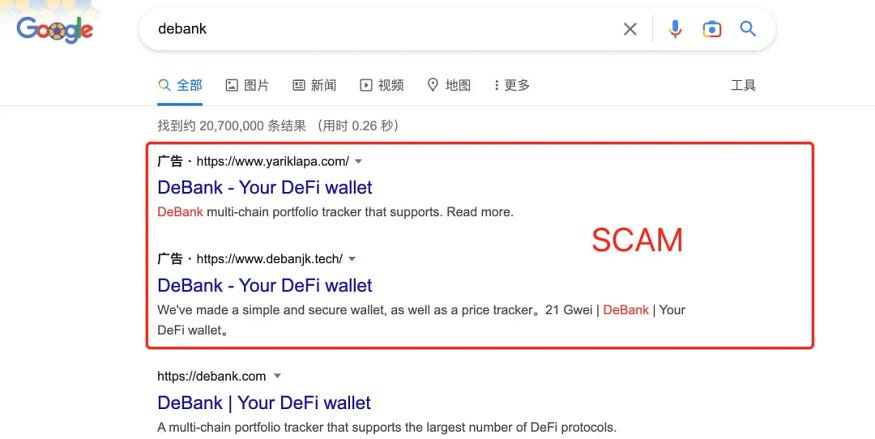
Search Engines
Rankings on Search engines can be purchased, leading to fake official websites ranking higher than the legitimate ones. Therefore, users should avoid searching for wallets directly through search engines and clicking on the top-ranked links. This practice could lead to a fake website where they might download a fraudulent wallet. When users are unsure of the official website’s URL, it is difficult to discern a fake site from the genuine one based solely on the website’s appearance. Fraudsters design fake websites to closely resemble official ones, making them almost indistinguishable. Similarly, users should not click on links shared by others on Twitter or other platforms, as these are often phishing links.
QR Codes from Friends/Scams
In the “dark forest” of Blockchain, it’s essential to maintain zero trust. Your friends or relatives may not intend to harm you, but the wallet they downloaded could be fake, and just hasn’t been compromised yet. When downloading a wallet using a QR code or link they shared, users could also end up with a fake wallet.
The SlowMist security team has received numerous reports of scams where scammers first gain the victim’s trust, then lead them to invest in cryptocurrency and share fake wallet download links. Ultimately, the victims suffer both emotional and financial losses. Therefore, users should be wary of online interactions, especially when someone encourages you to invest or sends you an unfamiliar link.
Telegram
On Telegram, searching for well-known wallets reveals several fake official groups. Scammers often claim that these groups are the official channels of certain wallets, even advising users to recognize the official website link, which turns out to be fake.
App Stores
It is important to note that apps in official app stores are not always safe. Some malicious individuals buy keyword rankings and use other tactics to lure users into downloading fraudulent apps. Readers should be vigilant and discerning when downloading apps.
So How Can Users Avoid Downloading Fake Wallets?
Official Website
The ability to find the official website is crucial, not just for downloading wallets but also for participating in other Web3 projects. Here’s how to locate the correct official website:
1. Twitter Verification
Users might search for the project on Twitter and judge its authenticity by follower count, registration time, and verification badges. However, these can be faked. We’ve discussed the sale of fake high-profile accounts in our article on phishing schemes. It’s advisable for beginners to follow security companies, industry experts, and reputable media on Twitter to see if they follow the account you’ve found.
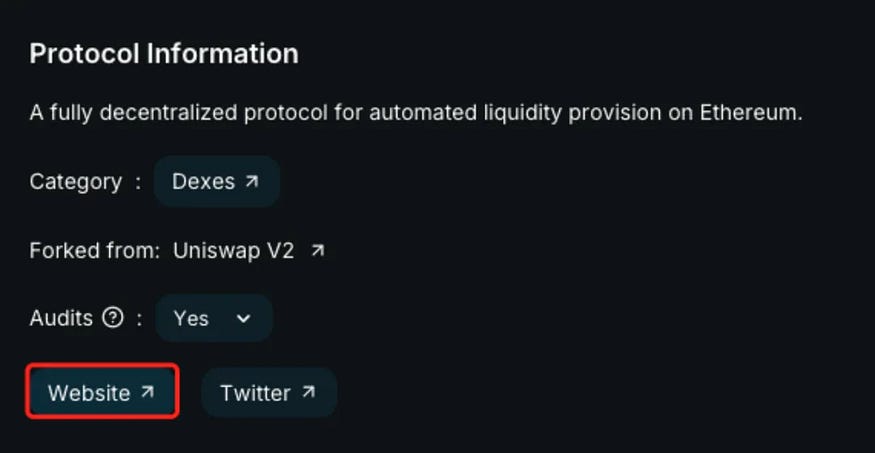
2. Cross-Verification
After finding the official Twitter account, further verification is needed since official accounts can be hacked. Compare the website link on the Twitter profile with links found on other reputable sources such as DefiLlama, CoinGecko, or CoinMarketCap:
https://defillama.com/
3. Bookmarking:
Once you have confirmed the official website, save the link to your bookmarks. This way, you can directly access the correct link next time, reducing the risk of visiting a fake website.
App Stores
Users can download wallets from official app stores like the Apple Store and Google Play Store. Before downloading, check the developer information to ensure it matches the official developer’s identity. Also, consider the app’s ratings and download counts.
Official Version Verification
To verify if the downloaded wallet is genuine, users can perform a file integrity check by comparing the file’s hash value. Drag the downloaded APK file into a file hash verification tool, which uses hash functions (e.g., MD5, SHA-256) to generate the hash value. If it matches the official hash value, it’s a genuine wallet. If not, it’s fake. Here’s what to do if you’ve downloaded a fake wallet:
1. Determine the Extent of the Leak: If you have downloaded a fake wallet but have not entered your private key or mnemonic phrase, simply delete the app and download the official version from the official website.
2. Private Key/Mnemonic Phrase Compromised: If you have entered your private key or mnemonic phrase into the fake wallet, it means your key/phrase has been compromised. Download the official wallet from the official website, import your private key/mnemonic phrase, and create a new address to quickly transfer your assets.
3. Stolen Cryptocurrency: If your cryptocurrency has been stolen, we offer free community assistance for case evaluation. You need to submit a form according to the incident type (funds stolen/scam/ransom). The hacker address you provide will also be shared with the InMist Threat Intelligence Network for risk control.
- Chinese Form: https://aml.slowmist.com/cn/recovery-funds.html
- English Form: https://aml.slowmist.com/recovery-funds.html
Purchasing Fake Hardware Wallets
We’ve discussed the risks of downloading fake wallets and their solutions. Now, let’s talk about why some users end up purchasing fake hardware wallets.
Some users choose to buy hardware wallets from online marketplaces, but these non-officially authorized stores pose significant security risks. It’s uncertain how many hands the wallet has passed through or if its internal components have been tampered with before reaching the user. Any tampering with the internal components is difficult to detect from the exterior or the wallet’s functionality.
How to Avoid Hardware Wallet Supply Chain Attacks:
1. Purchase from Official Channels: This is the most effective way to avoid supply chain attacks. Do not buy hardware wallets from unofficial channels such as online marketplaces, resellers, or through individuals.
2. Inspect the Packaging: Check for any signs of tampering on the packaging. Although it’s unlikely for hackers to expose themselves at this stage, it’s a basic precaution.
3. Official Device Verification: Some hardware wallets offer official device verification services. During the initialization, the device prompts users to verify it on the official website. If the device has been tampered with during transport, it won’t pass this verification.
4. Tamper-Evident Mechanisms: Consider purchasing hardware wallets with tamper-evident mechanisms. These wallets trigger a self-destruct mechanism if someone tries to open and tamper with the internal components. All sensitive information in the secure chip will be automatically erased, rendering the device unusable.
Prevent Private Key/Mnemonic Phrase Leak Risks
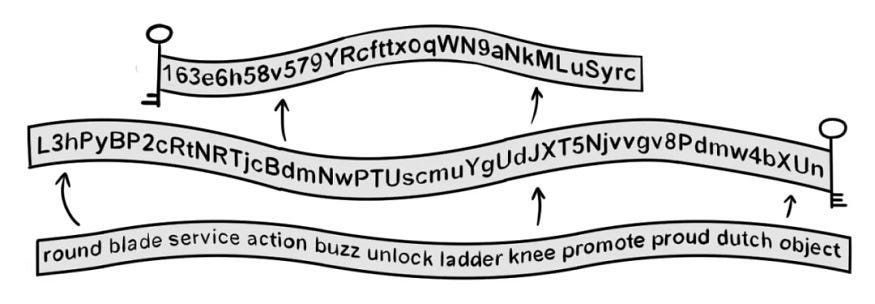
Having learned how to download or purchase genuine wallets, the next challenge is securely storing private keys/mnemonic phrases. These are the sole credentials for recovering your wallet and controlling your assets. A private key is a 64-character hexadecimal string, while a mnemonic phrase typically consists of 12 words. The SlowMist security team warns that if your private key/mnemonic phrase is compromised, your wallet assets are highly likely to be stolen. Here are common causes of leaks:
1. Improper Confidentiality: Users might share their private keys/mnemonic phrases with friends or family for safekeeping, resulting in theft by those individuals.
2. Storing or Transmitting Keys Online: Despite knowing better, some users store their private keys/mnemonic phrases via methods like WeChat favorites, photos, screenshots, cloud storage, or memos. If these platforms are hacked, the keys can be easily stolen.
3. Copying and Pasting Keys: Many clipboard tools and input methods upload clipboard records to the cloud, exposing private keys/mnemonic phrases to insecure environments. Malware can also steal clipboard information when keys are copied. Therefore, copying and pasting keys is risky.
How to Avoid Private Key/Mnemonic Phrase Leaks:
- Do Not Share: Never share your private key/mnemonic phrase with anyone, including friends and family.
- Physical Storage: Store private keys/mnemonic phrases on physical media to avoid network attacks. Write them on high-quality paper (and possibly laminate it) or use a metal mnemonic storage device.
Multi-Signature and Distributed Storage: Implement multi-signature setups and distribute storage locations to enhance security. For more detailed backup methods, refer to SlowMist’s Blockchain Dark Forest Self-Guard Handbook
Conclusion
This article covered the risks associated with downloading or purchasing wallets, methods to find and verify genuine websites, and the risks of private key/mnemonic phrase leaks. We hope this information helps you take the first step securely into the dark forest of blockchain. In the next issue, we’ll discuss wallet usage risks such as phishing, signatures, and authorization risks. Stay tuned. (Note: Brands and images mentioned are for illustrative purposes only and do not constitute recommendations or endorsements.)